Smart Refresh lets you fetch data for a large date range while periodically refreshing only a portion of that data. This approach significantly reduces query failures and improves overall query performance by minimizing the amount of data refreshed each time.
Working with large date ranges can be challenging, as queries may fail due to factors such as increased server load on the data platform. Smart Refresh addresses this by updating only a portion of the overall data, ensuring that each request sent to the data platform is smaller, more reliable, and less prone to failure.
This is especially useful when only a portion of the data changes over time. For example, you may want to query and incrementally store one year’s worth of Facebook data, but during refreshes, update only the most recent 14 days. Smart Refresh is ideal for this scenario as it allows you to retain historical data for years, continuously append new data, and refresh only the last 14 days that are subject to change. 14 days.
Here is how we can use Smart Refresh,
1. Before we begin, let’s make sure to enable Advanced scheduler access by going to My Account -> Preferences.
2. Create a new query or open an existing one that you want to work with.
3. Choose the metrics and dimensions that you need, but also make sure to add a “Date” dimension. Note that Smart Refresh requires selecting a Date dimension to function.
4. Specify the full date range for the data you wish to pull.
(Note: the feature only works if the date range is greater than 30 days.)
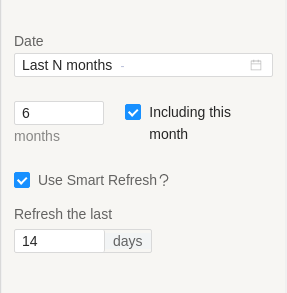
5. Enable Smart Refresh for the query, check the checkbox labeled Use smart refresh. You will notice a new field appear, prompting you to set the refresh period in days.
6. In the Refresh the last n days field, specify the desired refresh period. Refresh period determines which portion of the entire date range is updated during subsequent query runs.
7. Running the query now will fetch data for the entire specified date range and write it to the sheet initially.
8. Now if we save the query and rerun it, it will fetch data only for the refresh period we selected (i.e 14 days) and merge it with the existing dataset.
Lets go over a couple of examples where Smart Refresh comes handy
Example 1
Suppose you manage Facebook Ads campaigns and want to analyze performance within a 14-day or 28-day attribution window. With Smart Refresh, you can keep your data within these attribution windows consistently up to date by refreshing only the relevant recent period, without reprocessing the entire dataset.
For a 14-day attribution window, set the refresh period to 14 days. Each time the query runs, it will fetch and update data for the most recent two weeks, ensuring the data stays aligned with the attribution window.
Similarly, for a 28-day attribution window, set the refresh period to 28 days so that only the last 28 days of data are refreshed.
Example 2
Imagine you’re managing an e-commerce website and need to track daily sales performance. Running queries across several years of data can be slow and inefficient. Smart Refresh simplifies this by allowing you to focus on the most recent data, ensuring faster queries and up-to-date insights without repeatedly processing the entire historical dataset.
When setting up your query, define the complete date range you want to retrieve for example, the past two years. Then enable Smart Refresh and set the refresh period to the last 30 days.
On the first run, the query will fetch and write data for the entire two-year period. On subsequent runs, it will fetch and merge only the data from the most recent 30 days. This approach keeps your analysis up to date without repeatedly retrieving and processing the full historical dataset.
By using Smart Refresh in your query, you ensure that your historical data remains intact and up-to-date effortlessly. With each query execution, only the data within the defined refresh period will be fetched and refreshed in your spreadsheet.
Hope this was useful, please let us know if you have any feedback for us.